Coverages¶
This document describes the data model layout of the coverages, the internal structure of earth observation products, collections and data files. It also shows how these models can be interacted with via the command line interfaces.
Data model¶
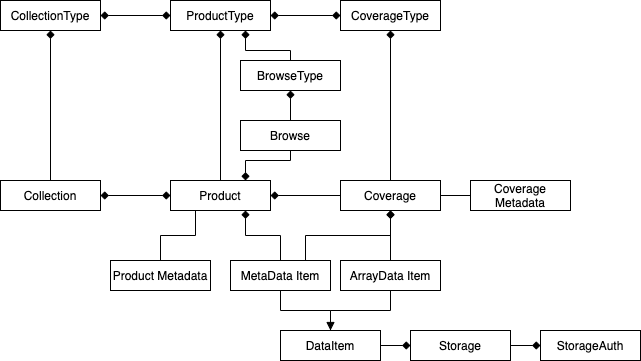
The data model is loosely based on the OGC coverages data models, especially with the EO Application Profile for WCS 2.0.
Coverage Type¶
The coverage type describes the internal structure of coverages of a specific type. The coverage type is comprised of a list of field types that define the structure and metadata of a specific field of Data, called the Field Type.
The coverage type has a unique name to allow its identification.
Product Type¶
The product type model allows to define the structure of products by limiting the coverage types each coverage is allowed to have for products of this product type.
Additionally, each Product Type can be associated with a number of Browse Type and Mask Type that define the masks and browses that products of that type are allowed to have.
Browse Type¶
A browse type defines a typical visual representation of a product. For this purpose, it allows to define expression, scaling ranges and nodata values to generate that representation (browse).
A browse type can either define a single output band (grey), three output bands (RGB) or four output bands (RGBA).
Expressions must follow Python syntax rules but can only contain simple arithmetic expressions. All identifiers must be names of field types that are linked to coverage types in the list of allowed coverage types of the referenced product type.
Mask Type¶
These type models define what polygon masks can be linked to products of that product type and whether the masks define areas of validity or invalidity.
Collection Type¶
These type models allow to define the shape of collections by allowing to limit the product types and coverage types of product and coverages that can be added to collections of their respective collection types.
EOObject¶
This is the base model class for uniquely identifier geospatial objects.
EOObject provides the fields identifier (mandatory and unique), the
footprint (its geometry) and its temporal distribution: begin_time and
end_time.
All objects inheriting from EOObject share a common pool of identifier. Thus, it is, for example, not possible for a collection to have the same identifier as a product or coverage.
Grid¶
A grid defines a regularly spaced grid comprised of up to four axes. Each axis can either be of spatial, temporal, evelation or other type. For each defined axis, the regular offset value must be specified.
Each grid is associated with a coordinate reference system.
A grid can be named, making it easier to manage.
A grid does not provide an actual location or area, this information can only be obtained with a Grid Fixture in conjunction with a grid.
Mosaic¶
This model is a collection of homogenenous coverages, all sharing the same coverage type and grid. This allows to access the mosaic as if it were a single coverage by combinig the data from all its comprising elements.
Coverage¶
A coverage is an n-dimensional raster data set comprised of several fields.
A coverage is linked to at least one ArrayDataItem, a reference to the actual raster data.
TODO: rel OGC coverage
Product¶
A product is a sort of collection of geospatially and temporally very close objects.
A product can combine multiple coverages which cover the same are but cannot be combined to a single coverage because of different resolutions.
In some cases, coverages are not necessary at all, and just provide data items for a binary download and browses for previewing.
Browse¶
A browse is always associated with a product and serves as a preview to the actual data. Browses are materialized files that are either pre-generated or can be generated from the coverage data.
Collection¶
Multiple coverages and products can be grouped in a collection. This relationship is many-to-many, so each product/coverage can be inserted into multiple collections.
When a collection is linked to a Collection Type only Products and Coverages whose types are of the set of allowed coverage/product types can be inserted.
Command Line Interfaces¶
The following command line interfaces can be executed via the manage.py
utility of the instance. All commands are related to one of the models above
and use sub-commands for specific tasks.
- coveragetype
This command manages Coverage Type models and allows to inspect the currently available ones.
- create
Creates a new Coverage Type with specifications from the parameters.
- name
- the name of the Coverage type to create
--field-type add a new field type to the definition. Must be the five parameters: identifier,description,definition,unit-of-measure, andwavelength. Can be used multiple times to add more than one field.TODO: example
- import
imports one or more Coverage Type definition from JSON files.
- locations*
- a list of filenames to import definitions from
--in, -i read from stdininstead from a fileTODO: show definitition, example
- delete
deletes a Coverage Type
- name
- the name of the Coverage Type to delete
--force, -f delete the Coverage Type, even if it is still in use. This cascades and deletes all Coverages of that type as well. - list
lists the stored Coverage Types
--no-detail disable the printing of details of the coverage type.
- producttype
This command manages Product Type models. It provides the following sub-commands:
- create
creates a new Product Type.
- name
- the name of the Product Type to create
--coverage-type the Coverage Type name to add to this product type. Can be specified multiple times. --mask-type the name of a to be created mask type. --validity-mask-type the name of a to be created validity mask type. --browse-type the name of a to be created Browse type. It is recommended to use browsetype createinstead.- delete
deletes a Product Type
- name
- the name of the Product Type to delete
- list
lists all available Product Types
--no-detail disable the printing of details of the product type.
- browsetype
This command allows to create, delete and list Browse Type models. Since Browse Types are always associated with a Product Type the first argument is always the name of a Product Type.
- create
creates a new Browse Type for a Product Type. Valid field names for the
--red,--green,--blue, and--alphaparameters are the names from the field names of the linked Coverage Types of the associated Product Type.- product_type_name
- the Product Type to create the Browse Type for
- [browse_type_name]
- the name of the Browse Type. Can be omitted, to define the default Browse Type.
--red, --grey, -r the field name or mathemathical expression to use as the red output band (or grey, if used for a single band output). --green, -g the field name or mathemathical expression to use as the green output band. --blue, -b the field name or mathemathical expression to use as the blue output band. --alpha, -a the field name or mathemathical expression to use as the green output band. --red-range, --grey-range the low and high border of values to apply a linear stretch for the red output band. --green-range the low and high border of values to apply a linear stretch for the green output band. --blue-range the low and high border of values to apply a linear stretch for the blue output band. --alpha-range the low and high border of values to apply a linear stretch for the alpha output band. --red-nodata, --alpha-nodata the nodata value for the red output band. This is applied after the stretch and will result in transparent pixels for this value. --green-nodata the nodata value for the green output band. This is applied after the stretch and will result in transparent pixels for this value. --blue-nodata the nodata value for the blue output band. This is applied after the stretch and will result in transparent pixels for this value. --alpha-nodata the nodata value for the alpha output band. This is applied after the stretch and will result in transparent pixels for this value. - delete
deletes a no longer needed Browse Type.
- product_type_name
- the Product Type to delete the Browse Type from
- [browse_type_name]
- the name of the Browse Type to delete
- list
lists all Browse Types for a given Product Type.
- product_type_name
- the Product Type to list the Browse Types for
- masktype
This command allows to create, delete and list Mask Type models. Since Mask Types are always associated with a Product Type the first argument is always the name of a Product Type. The sub-commands are in detail:
- create
creates a new Mask Type for a Product Type
- product_type_name
- the Product Type to create the Mask Type for
- mask_type_name
- the Mask Type name to create
--validity whether this mask denotes valid or invalid values. By default, it uses invalidity. - delete
deletes a Mask Type.
- product_type_name
- the Product Type to delete the Mask Type from
- mask_type_name
- the Mask Type name to delete
- list
lists all Mask Types for a given Product Type.
- product_type_name
- the Product Type to list the Mask Type of
- collectiontype
This command manages Collection Type models using the following sub-commands:
- create
creates a new Collection Type.
- name
- the name of the Collection Type
--coverage-type, -c the name of an existing Coverage Type, that shall be linked to this Collection Type. Only Coverages can be inserted into Collection when the Coverages Type is part of the Collections Type. --product-type, -p the name of an existing Product Type, that shall be linked to this Collection Type. Only Products can be inserted into Collection when the Product Type is part of the Collections Type. - delete
deletes a Collection Type.
- name
- the name of the Collection Type to delete
--force, -f forces the deletion of all still existing Collections using this Collection Type. - list
lists all available Collection Types.
--no-detail Disable the printing of details of the Collection types.
- grid
This command allows to create and delete named Grid Model instances.
- create
this creates a Grid.
- name
- the name of the Grid to create
- coordinate_reference_system
- the definition of the coordinate reference system. Either an integer (the EPSG code), or the URL, WKT or XML definiton.
The following parameters can be used up to four times in order to define multiple axes.
--name, --axis-name, -n the name of the n-th axis to add to the Grid. --type, --axis-type, -t the type of the n-th axis to add to the Grid. --offset, --axis-offset, -o the fixed axis offset step of the n-th axis to add to the Grid. - delete
deletes a Grid.
- name
- the name of the Grid to delete.
- coverage
this command allows the registration and deregistration of Coverage Model instances.
- register
this sub-command registers a Coverage.
--data, -d this specifies a location for raster data. Multiple values can be used to denote that the data resides on a storage. If used in that way the first value can also be the name of a named storage. This parameter can be used multiple times, when the raster data is split into multiple files. --meta-data, -m similarly to the --dataparameter, this parameter denotes a reference to meta-data. The same rules as for the--dataparameter also apply here.--type, --coverage-type, -t specify the Coverage Type for this Coverage. By default no Coverage Type is used. --grid, -g specify the named Grid Model to use. By default an anonymous Grid is used with the CRS of the raster data files. --size, -s specifies the size of the Coverage. This overrides the size extracted from the metadata/data. Must specify the size for each axis of the Grid. --origin, -o overrides the origin of the Coverage. Must provide a value for each axis of the Grid. --footprint, -f overrides the geographical footprint of the Coverage. Must be a valid WKT geometry. --footprint-from-extent The footprint polygon shall be calculated from the Coverages extent. --identifier, -i override the Coverages identifier. --identifier-template allows the construction of the final identifier from a template. Substitution values are passed in from the extracted metadata. e.g: {identifer}__B01.--begin-time, -b override the begin timestamp of the Coverage. Must be a valid ISO 8601 datetime string. --end-time, -e override the end timestamp of the Coverage. Must be a valid ISO 8601 datetime string. --product, --product-identifier, -p specify the Product identifier this Coverage shall be associated with. The Product must already be registered. --collection, --collection-identifier, -c specify the Collection identifier this Coverage shall be inserted into. The Collection must already exist. --replace, -r replace an already existing Coverage with the same identifier. --use-subdatasets, --subdatasets specify to interpret colons in the filename as subdataset specifiers. --print-identifier this switch prints the final identifier (after metadata extraction and potential templating) to stdout upon successful registration. - deregister
this sub-command de-registers the Coverage with the provided identifier.
- identifier
- the Coverages identifier
--not-refresh-collections this command will update all Collections metadata (footprint, begin-/end time) unless this switch is set. --all, -a When this flag is set, all the Coverages are selected to be derigesterd.
- product
this command manages Product Model instances.
- register
this sub-command registers products.
--identifier, -i override the Product identifier. --identifier-template allows the construction of the final identifier from a template. Substitution values are passed in from the extracted metadata. e.g: {identifer}__B01.--footprint overrides the geographical footprint of the Product. Must be a valid WKT geometry. --begin-time override the begin timestamp of the Product. Must be a valid ISO 8601 datetime string. --end-time override the end timestamp of the Product. Must be a valid ISO 8601 datetime string. --set, -s sets a specific metadata value for that product. This parameter always uses two values: the name of the parameter key and its value. TODO: possible metadata keys to set --metadata-file adds a metadata file to the product. As with file links for Coverages, the product file can be located on a storage. For these cases, multiple values can be used to specify the chain of locations. --type, --product-type, -t specify the Product Type for this Product. By default no Product Type is used. --mask, -m specify a mask file to be added to this product. Must be two values: the masks name and its file location. --mask-geomety, -g specify a mask using its geometry directly. Must be two values: the masks name and its WKT geometry representation. --no-extended-metadata when this flag is set, only the basic metadata (identifier, footprint, begin- and end-time) is stored. --no-masks when this flag is set, no masks will be discovered. --no-browses when this flag is set, no browses will be discovered. --no-metadata when this flag is set, no metadata files will be discovered. --package specify the main data package for this Product. --collection, --collection-identifier, -c specify the Collection identifier this Product shall be inserted into. The Collection must already exist. --replace replace an already existing Product with the same identifier. --print-identifier this switch prints the final identifier (after metadata extraction and potential templating) to stdout upon successful registration. - deregister
deregisters a Product.
- identifier
- the identifier of the Product to deregister.
--all, -a When this flag is set, all the Coverages are selected to be derigesterd. - discover
print the contents of the main package file of a Product.
- identifier
- the identifier of the Product to discover.
- [pattern]
- a filename glob pattern to filter the resulting filenames
- browse
this command allows to manage Browse Model instances of a Product Model.
- register
this sub-command registers a Browse to a Product.
- identifier
- the Product identifier to register the Browse for.
- location
- the storage location of the Browse.
--type the Browse Type name of that Browse. - generate
- TODO
- deregister
- TODO
- mask
this command allows to manage Mask Model instances of a Product Model.
- register
registers a Mask for a Product.
- identifier
- the Product identifier to register the Mask for.
--type the Mask Type name of that Mask. --location the storage location of the Mask. --geometry the inline WKT geometry for the mask. - deregister_parser
deregisters a Mask from a Product
- identifier
- the Product identifier to deregister the Mask from.
- collection
this command manages Collection Model instances. As usual, it uses sub-commands to allow fine control over the specific aspects and tasks of a Collection.
- create
creates a new Collection.
- identifier
- the identifier for the new Collection.
--type, -t specify a Collection Type for this new Collection. --grid, -g specify a Grid for this Collection. --set, -s set or override Collection metadata. TODO: what keys? - delete
this sub-command deletes a Collection.
- identifier
- the identifier of the Collection to delete
--all, -a When this flag is set, all the collections are selected to be derigesterd. - insert
with this sub-command one or more Coverage Model instances or Product Model instances can be inserted into the collection. This command checks whether the to be inserted objects are of the allowed types when a Collection Type is set for this Collection.
- identifier
- the identifier of the Collection to insert objects into.
- object_identifiers+
- the list of object identifiers (either Products or Coverages) to insert into the Collection.
- exclude
this command allows to remove one or more objects from a collection.
- identifier
- the identifier of the Collection to exclude objects from.
- object_identifiers+
- the list of object identifiers (either Products or Coverages) to exclude from the Collection.
- purge
this command purges all Coverages and Products from this Collection, leaving it effectively empty.
TODO: not yet implemented
- summary
collects metadata from all entailed Products and Coverages to generate a summary that is stored in the Collection. This allows a quick overview of the metadata ranges and specific values of all objects in the collection.
- identifier
- the Collection identifier to generate the summary for
- –products/–no-products
- whether or not to generate a Product metadata summary.
- –coverages/–no-coverages
- whether or not to generate a Coverage metadata summary.
- mosaic
this command manages Mosaic Model instances with a variety of sub-commands.
- create
creates a new Mosaic.
- identifier
- the identifier of the Mosaic to create.
--type, -t the Coverage Type name for the Mosaic to create. --grid, -g the Grid to use for the Mosaic. - delete
deletes a Mosaic.
- identifier
- the identifier of the Mosaic to delete.
- insert
insert one or more Coverages into the Mosaic.
- identifier
- the identifier of the Mosaic to insert Coverages into.
- coverage_identifiers+
- the Coverage identifiers to insert into the Mosaic.
- exclude
exclude one or more Coverages from the Mosaic.
- identifier
- the identifier of the Mosaic to exclude Coverages from.
- coverage_identifiers+
- the Coverage identifiers to exclude from the Mosaic.
- refresh
refresh the summary metadata of the Mosaic.
- identifier
- the identifier of the Mosaic to generate the metadata.
- purge
- TODO not implemented
- id
this command allows to introspect the contents of the instances database.
- check
this subcommand allows to check whether or not an object is registered. The return value of this command indicates whether such an object exists.
- identifiers+
- the identifier(s) to check for existence.
--type, -t limit the check to the given object type (i.e: Coverage,Product,Collection, orMosaic). By default the search is for anyEOObject.- list
this command lists the contents of the database and prints the objects on on the terminal. Filters can be applied to limit the search.
- identifiers*
- limit the output to the given identifiers.
--type, -t limit the listing to the given object type (i.e: Coverage,Product,Collection, orMosaic). By default the search is for anyEOObject.--recursive, -r do a recursive lookup into the given collections. --suppress-type, -s when printing an object, suppress the type and only print the identifier --collection, -c limit the search to this collection only. Can be passed multiple times to search across multiple collections.
- mapcache
this command allows to generate an index database to be used for mapcache time dimensions.
- sync
this sub-command synchronizes a mapcache index database. The output will be written to the
<collection-name>.sqlitefiles for each available collection in the current working directory.The schema of the database will be the following:
CREATE TABLE "time" ( "start_time" timestamp with time zone NOT NULL, "end_time" timestamp with time zone NOT NULL, "minx" double precision NOT NULL, "miny" double precision NOT NULL, "maxx" double precision NOT NULL, "maxy" double precision NOT NULL )
--force, -f force the re-generation of the index files. --unique-times, -u force unique time entries. This combines the extent of all objects with overlapping time spans. --no-index this flag prohibits the creation of an internal database index.
- stac
This command allows to register Products and their related data from `STAC Items`_.
- register
this sub-command registers a STAC Item as a Product and its raster data as Coverages.
--in, -i Read the STAC Item from stdin instead from a file. --type TYPE_NAME, --product-type TYPE_NAME, -t TYPE_NAME The name of the product type to associate the product with. Optional. --replace, -r Optional. If the product with the given identifier already exists, replace it. Without this flag, this would result in an error. - types
this sub-command extracts all the relevant information to generate Product Types, Coverage Types and their related types to allow a subsequent registration.
--in, -i read the STAC Item from stdin instead from a file. --type TYPE_NAME, --product-type TYPE_NAME, -t TYPE_NAME the name of the new product type. Optional.